Can We Predict Solar Storms?
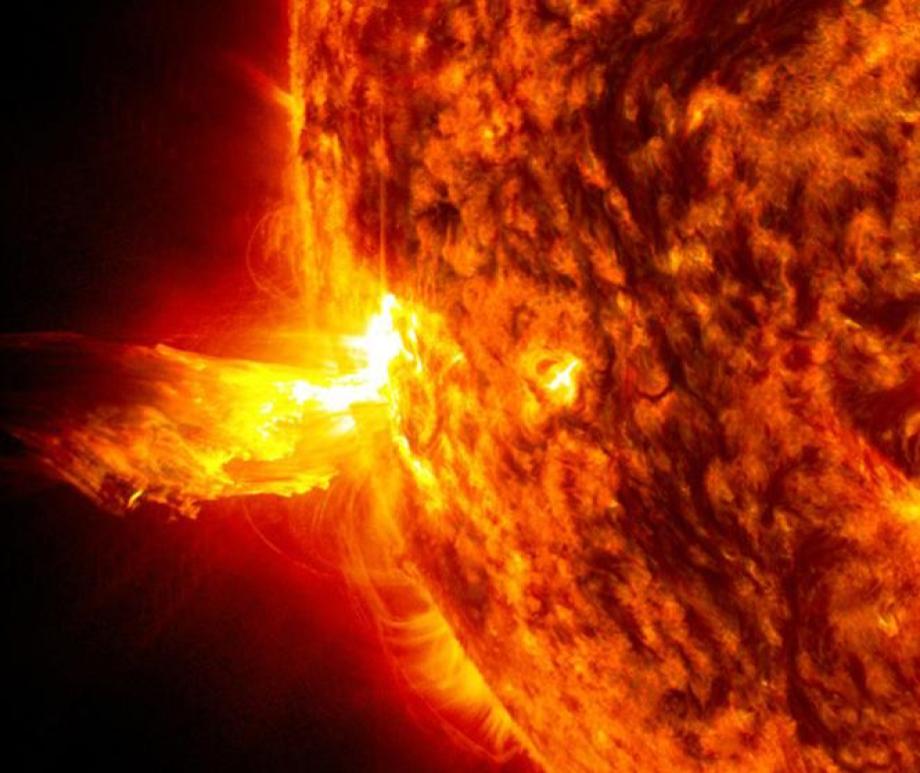
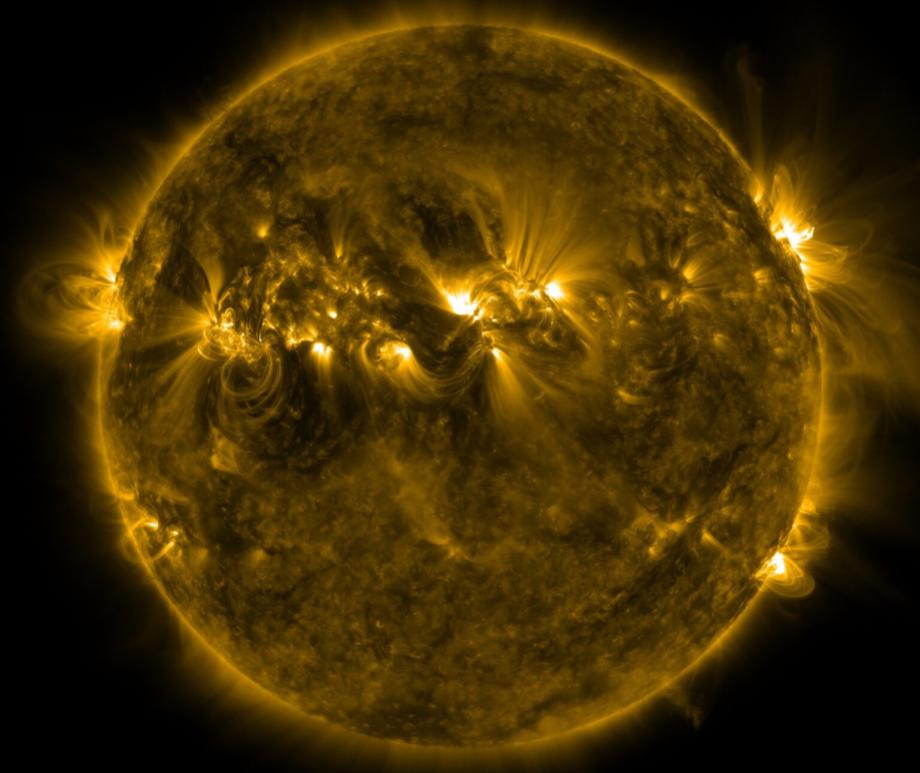
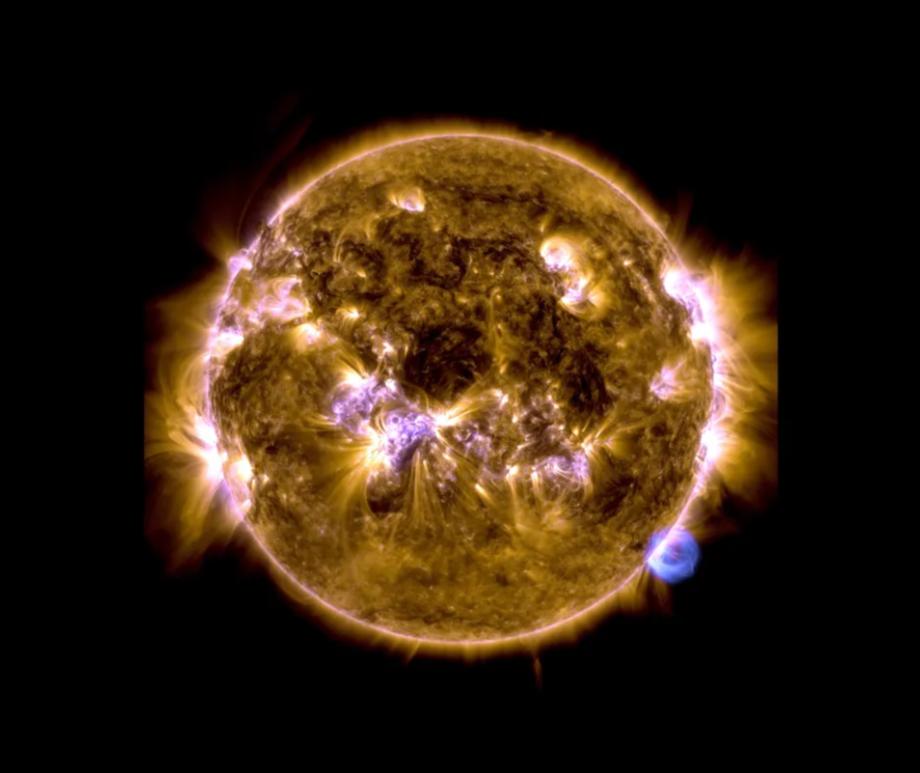
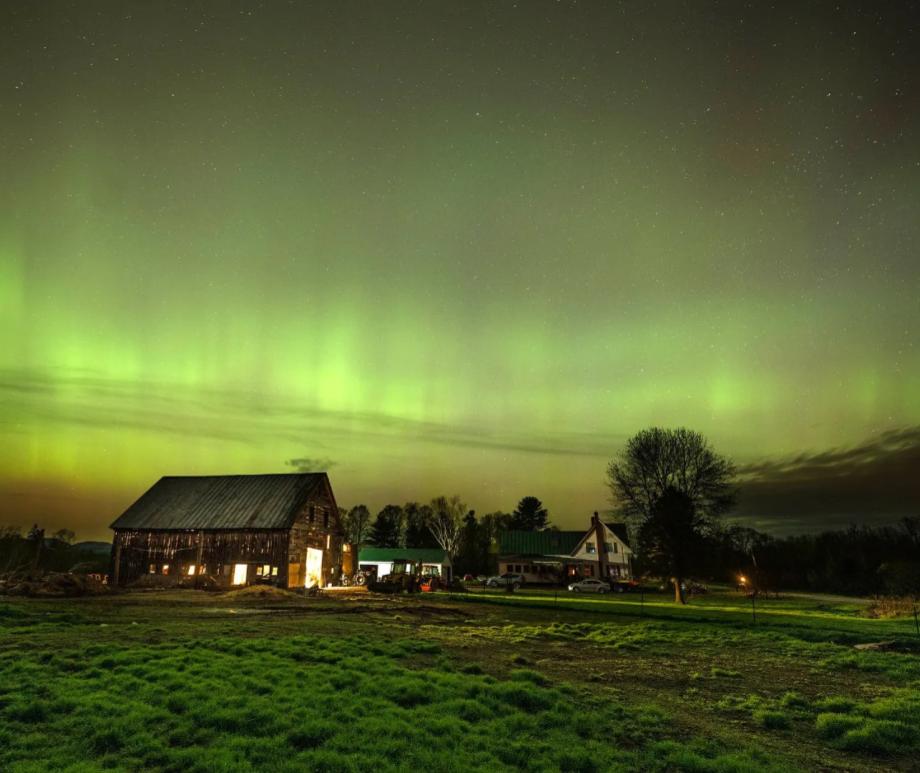
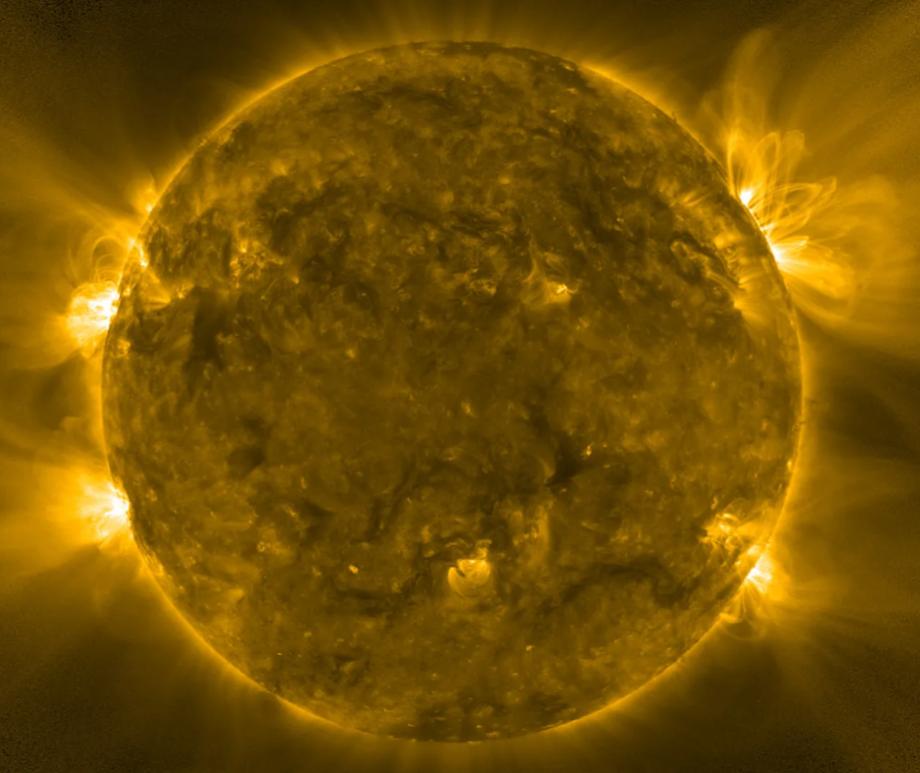
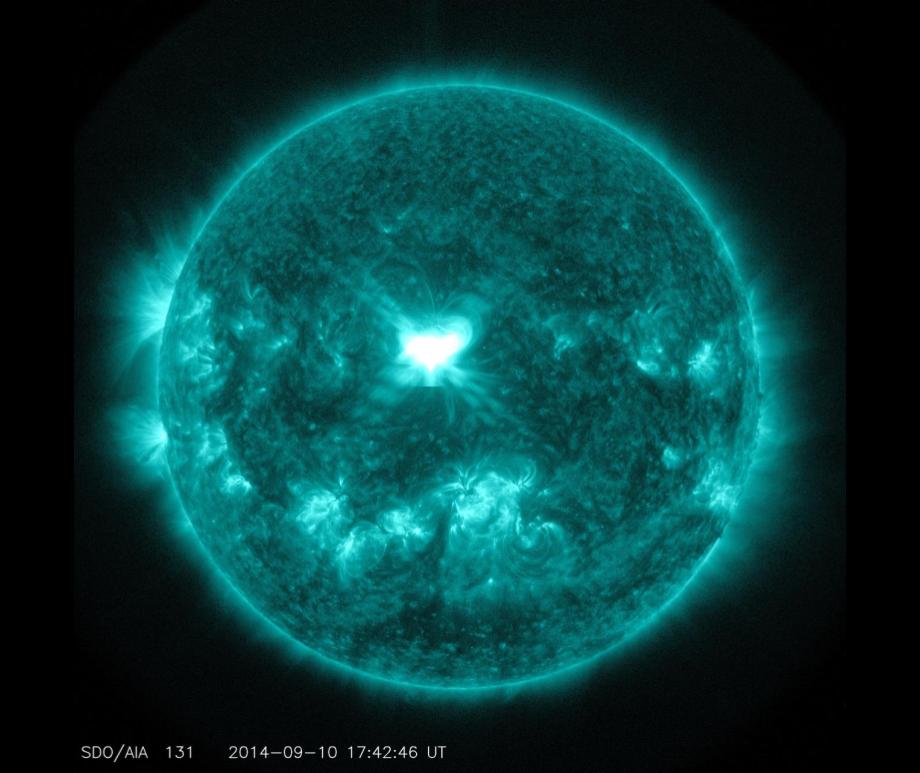
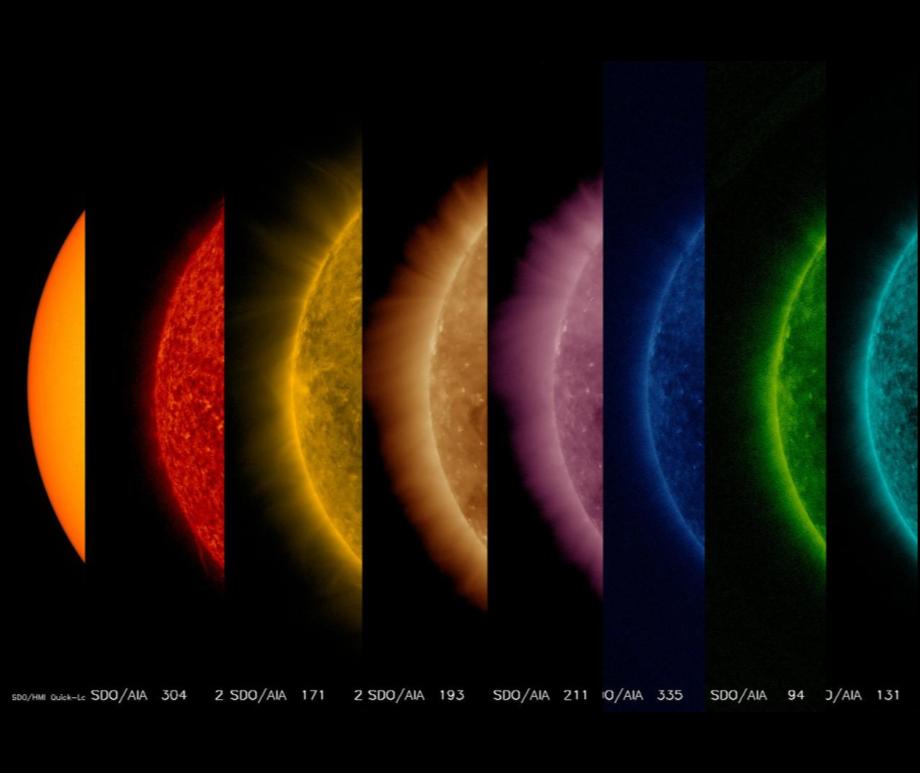
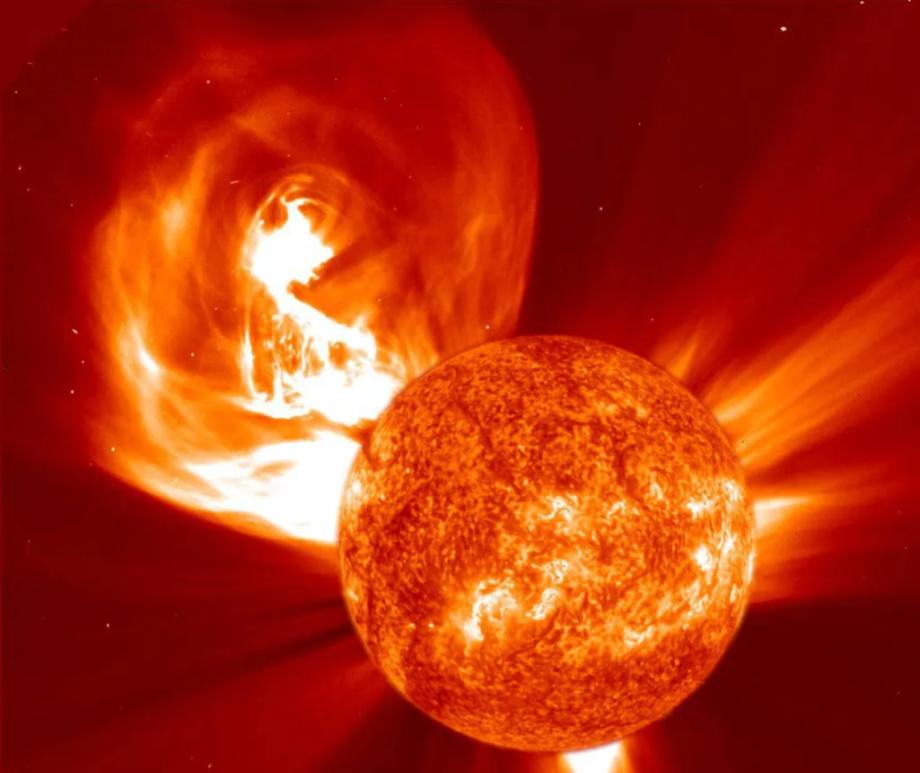
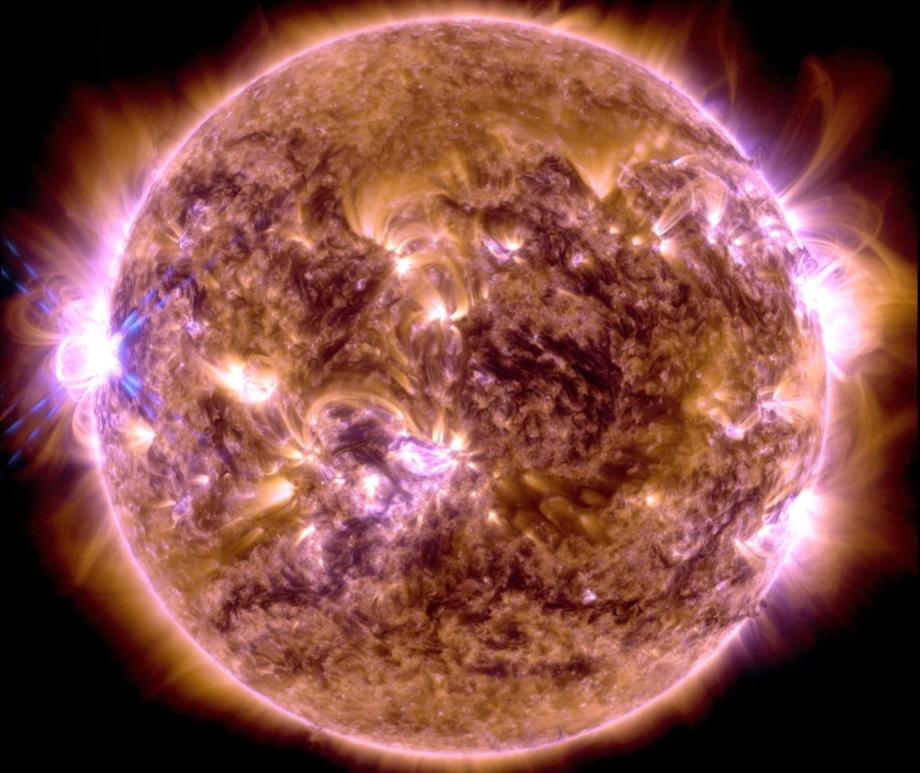
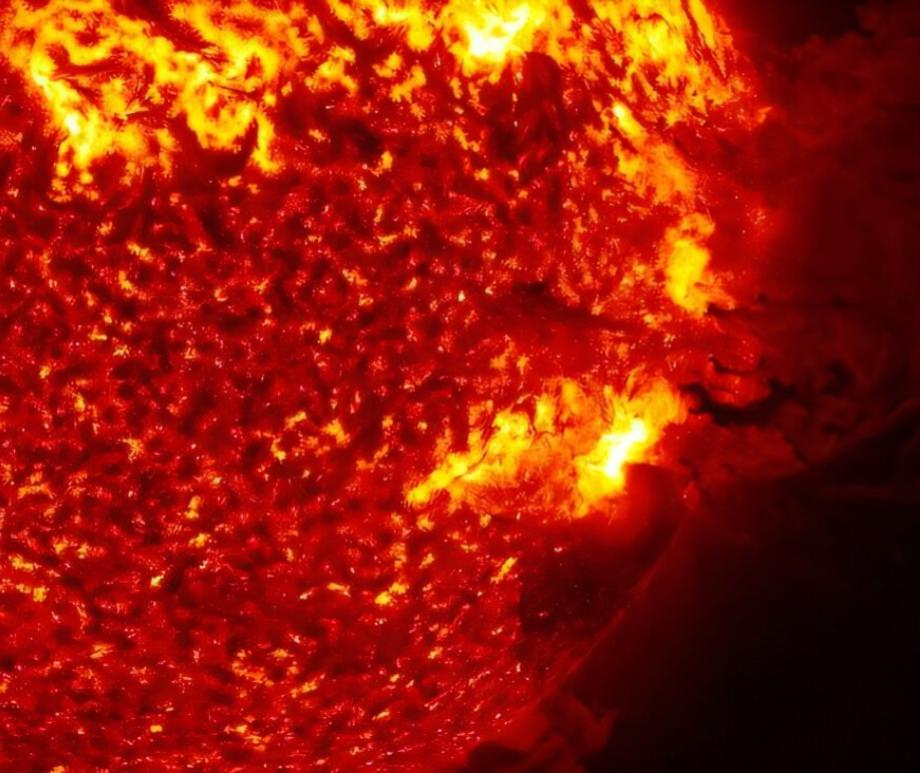
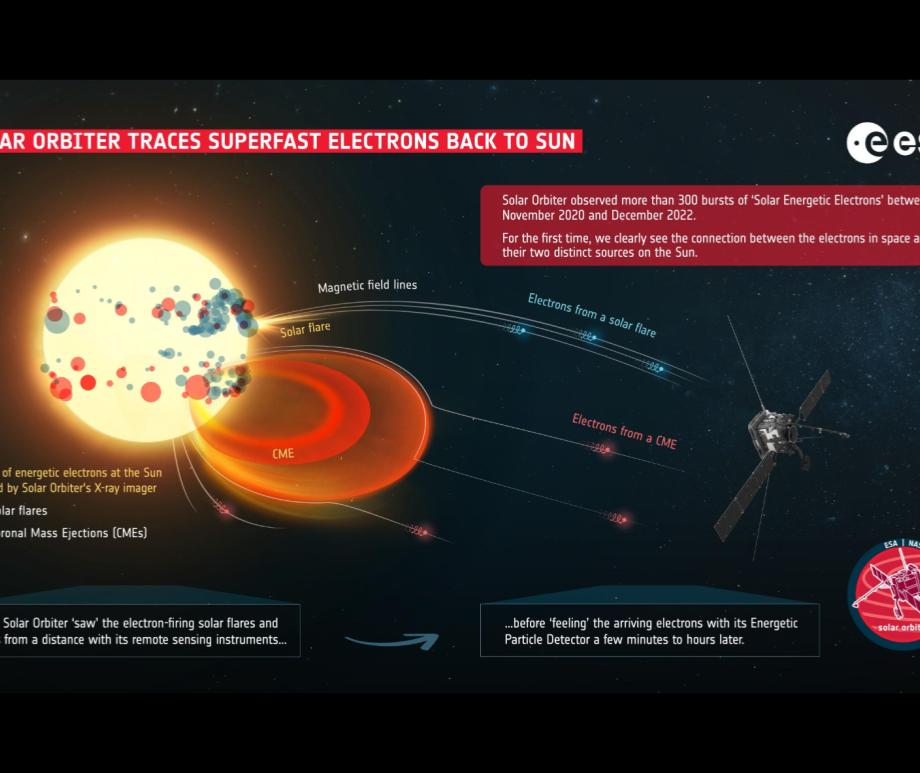
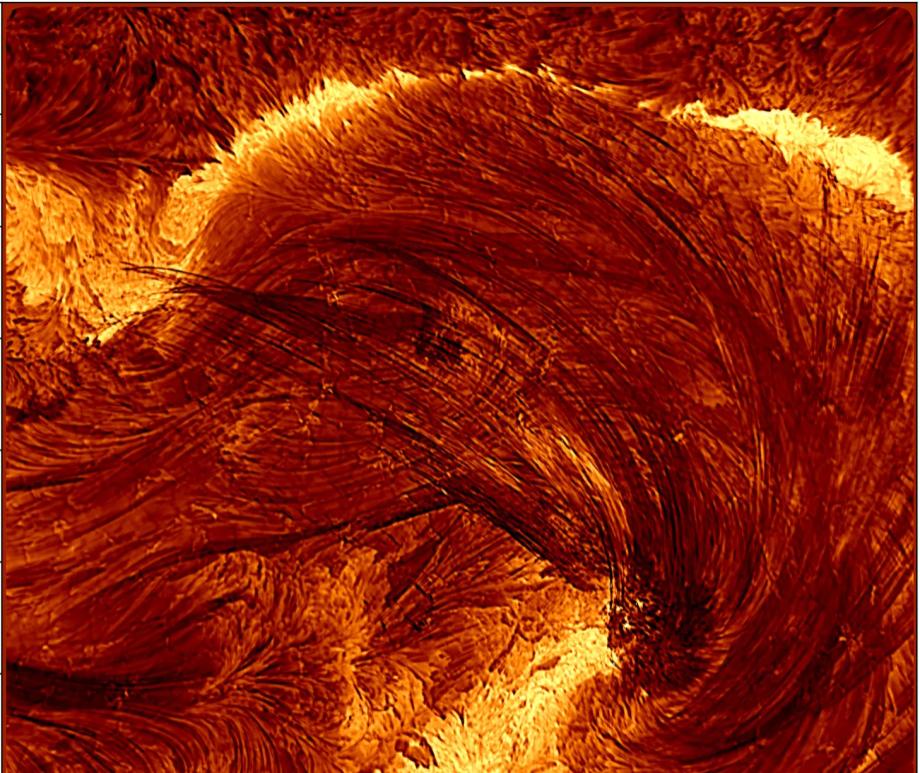
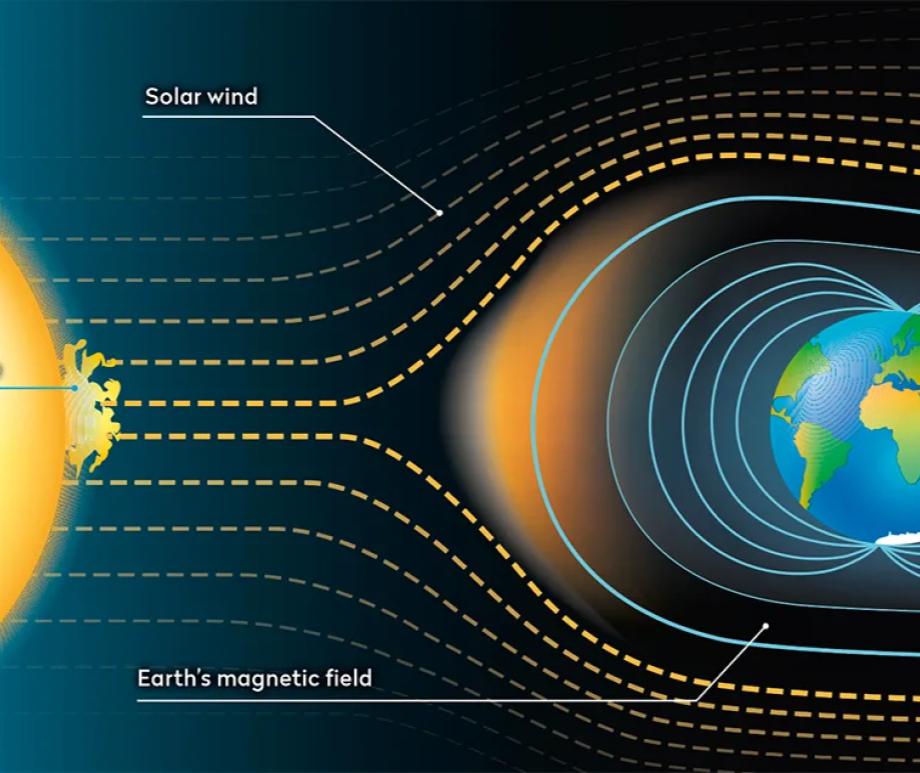
When you think of natural disasters, things like hurricanes and earthquakes come to mind. Though massive solar storms are far less common, they can be even more dangerous to life as we know it. The strongest storm on record, the Carrington Event in 1859, ignited fires at telegraph stations and shut down all communications on these lines. The solar flare responsible for the storm was briefly brighter than the Sun itself and caused aurora in the tropics! If a storm that strong occurred now, it could shut down power grids, communication satellites, phone lines, and radar stations around the world. That’s why being able to predict storms is crucial to giving us time to brace for the effects and minimize damage. Using data from spacecraft observing the Sun together with AI technology, NASA can now issue warnings 30 minutes before a storm will strike, as well as where effects will be the worst, and they continue to improve their capabilities. Read More
Latest News About The Sun
Fascinating Facts About The Sun
- The energy Earth receives from the Sun is 10,000 times the total world energy use, or about 48,000,000,000 kWh every second. Look at your electricity bill. How many kWh did you use last month? Divide that by 2,600,000 to get the kWh you used each second.
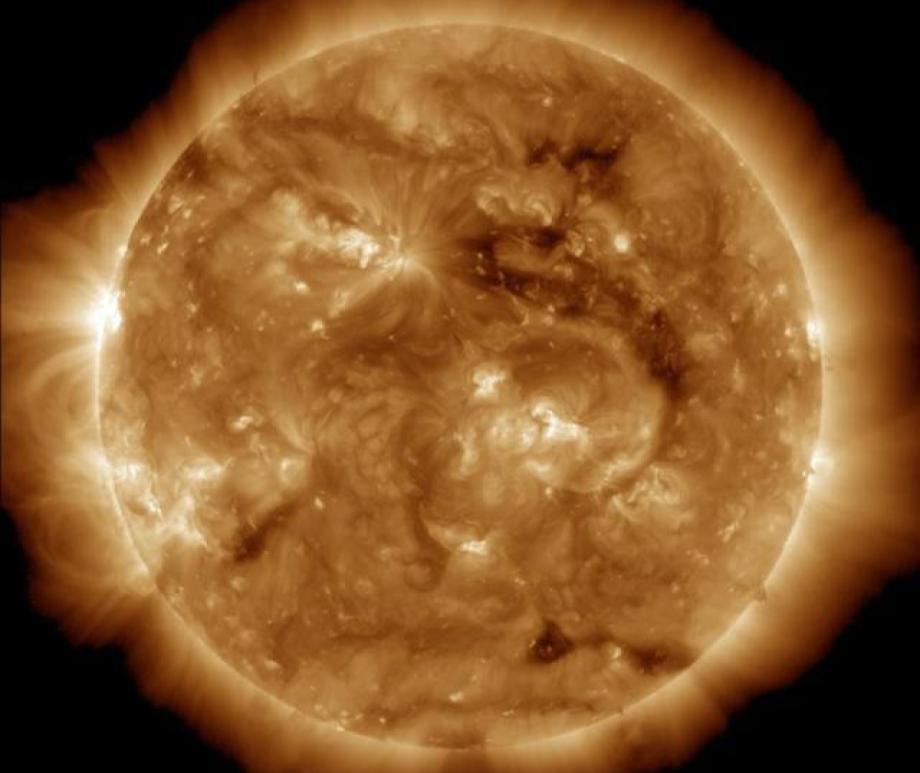
- It is a ball of plasma (super-heated gas) composed almost entirely of hydrogen and helium, with trace amounts of other elements that were produced by much more massive stars and then distributed throughout the galaxy when those stars exploded.
- Its core, which is 15,000,000°C, is 13 times denser than lead. The nuclear fusion happening there is the source of all the Sun's energy.
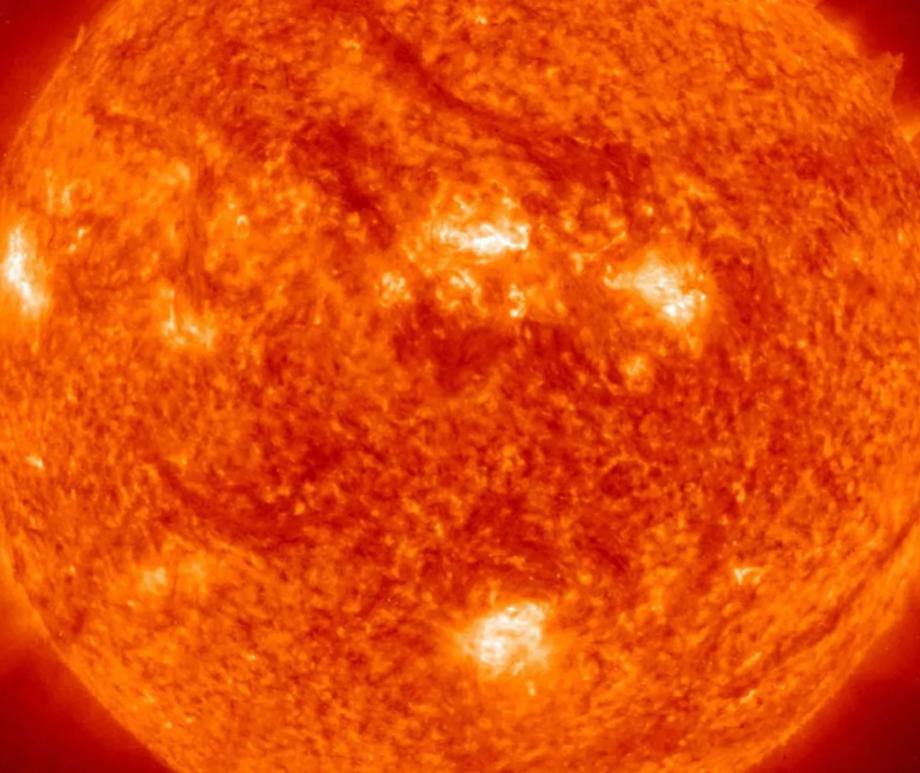
- The 'surface of the Sun' is a thin layer called the photosphere, which is 5,500°C. It's where all the sunlight we receive comes from, and what defines the shape of the Sun we see in the sky.
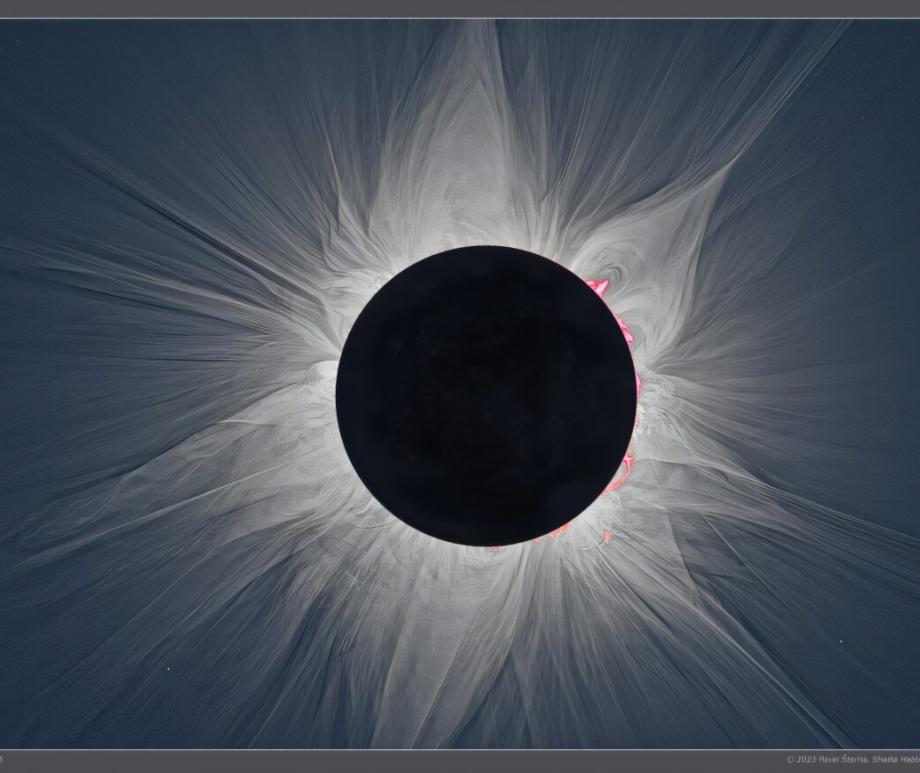
- Its outer atmosphere, called the corona, can be as hot as 1,000,000°C. It can only be seen by human eyes during a total solar eclipse, when the photosphere is blocked by the Moon. Except for during totality of an eclipse, NEVER look directly at the Sun without specialized eclipse-viewing glasses sold by a reputable scientific equipment company.
- Its light is essentially white to our eyes, having only an imperceptibly higher amount of yellow light in it. Fresh, pure snow reflects over 90% of visible light, so it closely resembles the color of sunlight.
- Though its size is small among all types of stars, it is much bigger than most of the stars around us, since smaller red dwarf stars dominate our galaxy.
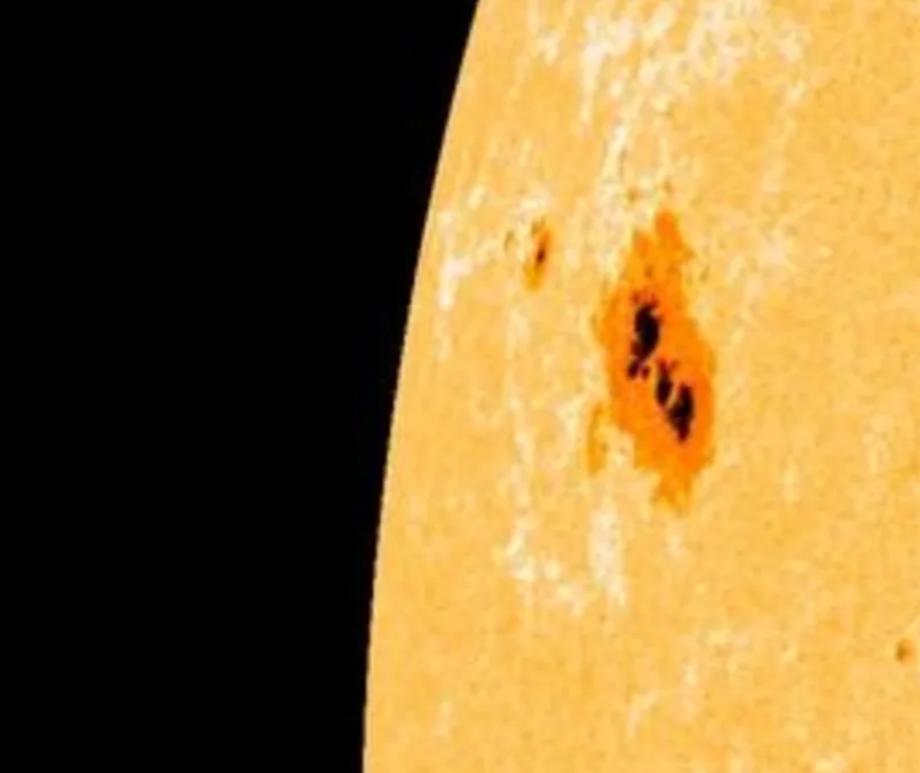
- Every 11 years, it reverses its magnetic polarity: its north pole becomes a south pole, and vice versa. During this change, solar activity is higher, creating more sun spots, flares, and eruptions.
- It takes light over 100,000 years to get from the Sun's core to its surface, traveling through the dense layers of plasma. It would take about 2 seconds for light to move that distance through empty space. It then takes 8 minutes and 20 seconds to get to Earth.
Sources: NASA, US Department of Energy, US Energy Information Administration
Missions
Solar Orbiter (2020)
Taking the closest ever images of the Sun, it is studying its 11-year cycle, the temperature of the corona, and the solar wind
Parker Solar Probe (2018)
Getting 7 times closer to the Sun than any previous spacecraft, it is exploring the Sun’s atmosphere by flying through it at 430,000 mph
DSCOVR (2015)
The Deep Space Climate Observatory monitors changes in the solar wind, providing space weather alerts and forecasts for geomagnetic storms that could disrupt power grids, satellites, telecommunications, aviation and GPS
IRIS (2013)
The Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph observes how solar material produces energy that heats up the Sun’s atmosphere
Solar Dynamics Observatory (2010)
Studies the Sun’s energy, the workings inside the Sun and how energy is stored and released
STEREO (2006)
The Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory, a pair of spacecraft, has provided stereoscopic measurements to study the Sun, space weather and coronal mass ejections
ACE (1997)
The Advanced Composition Explorer contributes to our understanding of the Sun, its interaction with Earth, and the evolution of the Solar System
SOHO (1996)
The Solar and Heliospheric Observatory is investigating the Sun's core, corona, and solar wind; it also makes comet discoveries
Ulysses (1990)
Observed the north and south poles of the Sun through a series of passes in 1994/1995, 2000/2001, and 2007/2008
Helios A&B (1974-1976)
Observed solar wind, magnetic and electric fields, cosmic rays and cosmic dust between Earth and the Sun
Pioneer 6-9 (1965-1968)
A network of solar-orbiting "space weather" monitors, observing solar wind, cosmic rays, and magnetic fields; a few are still functional