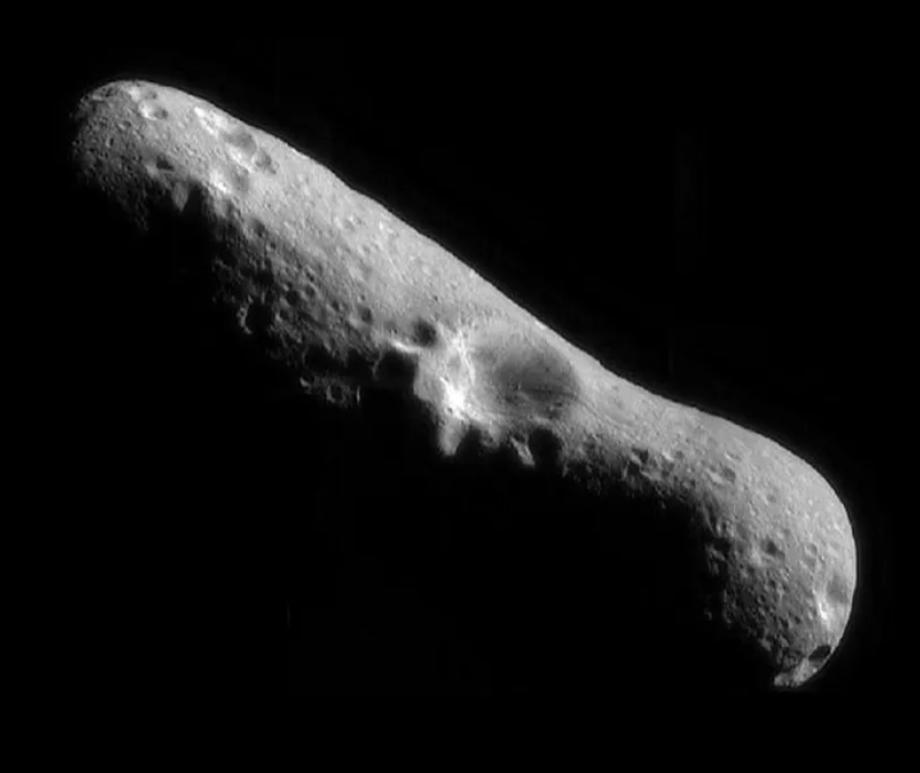
MAIN ASTEROID BELT
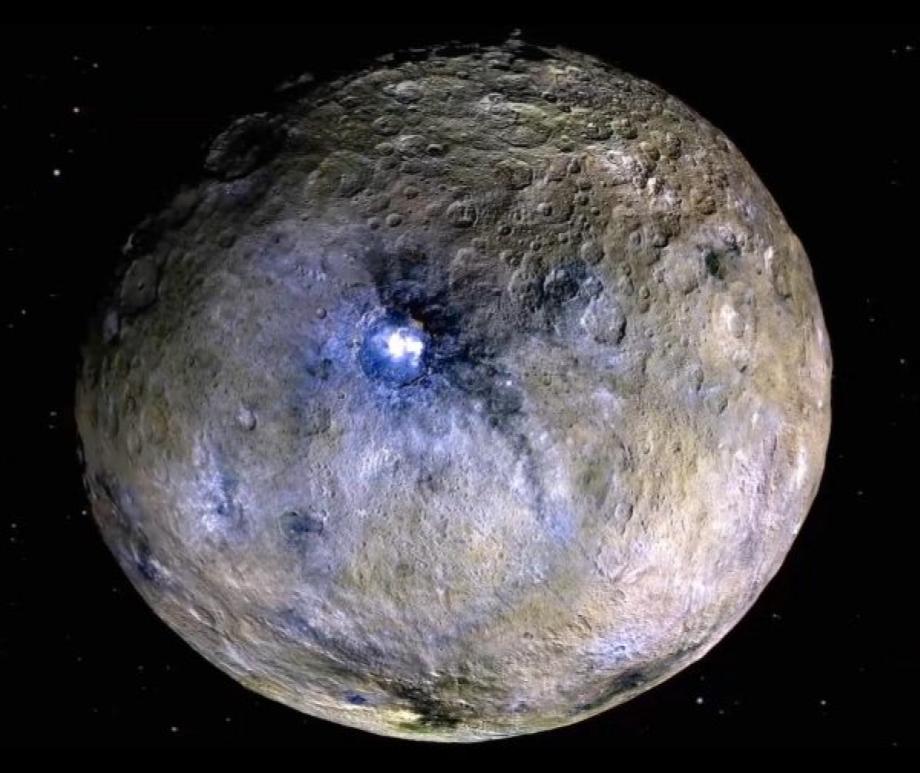
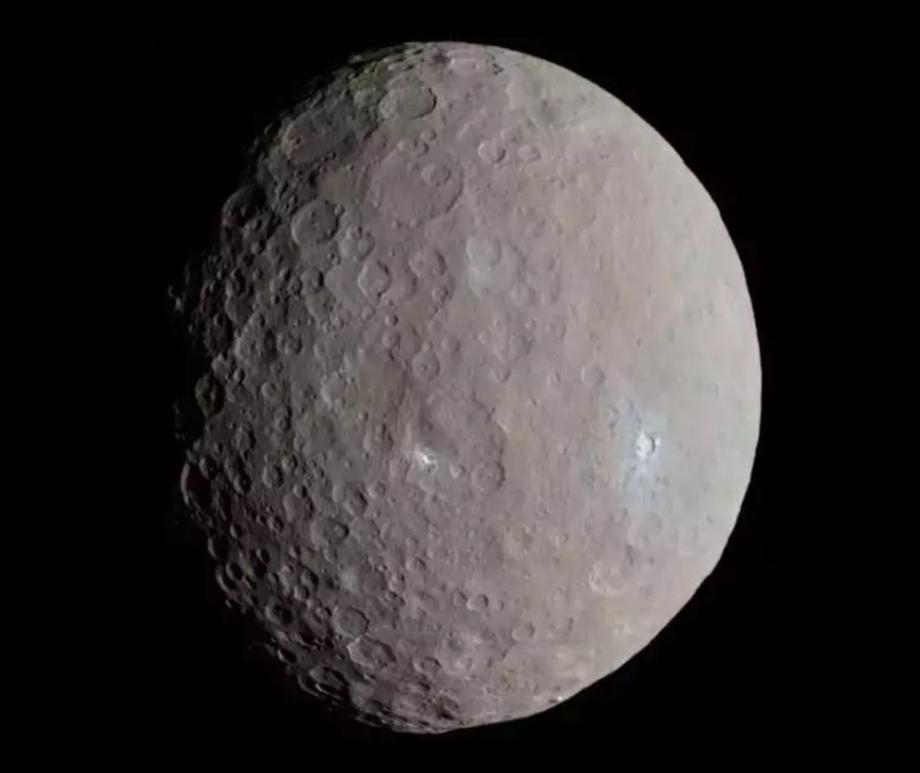
Planetary leftovers, ruled by Ceres
How Can We Protect Earth?
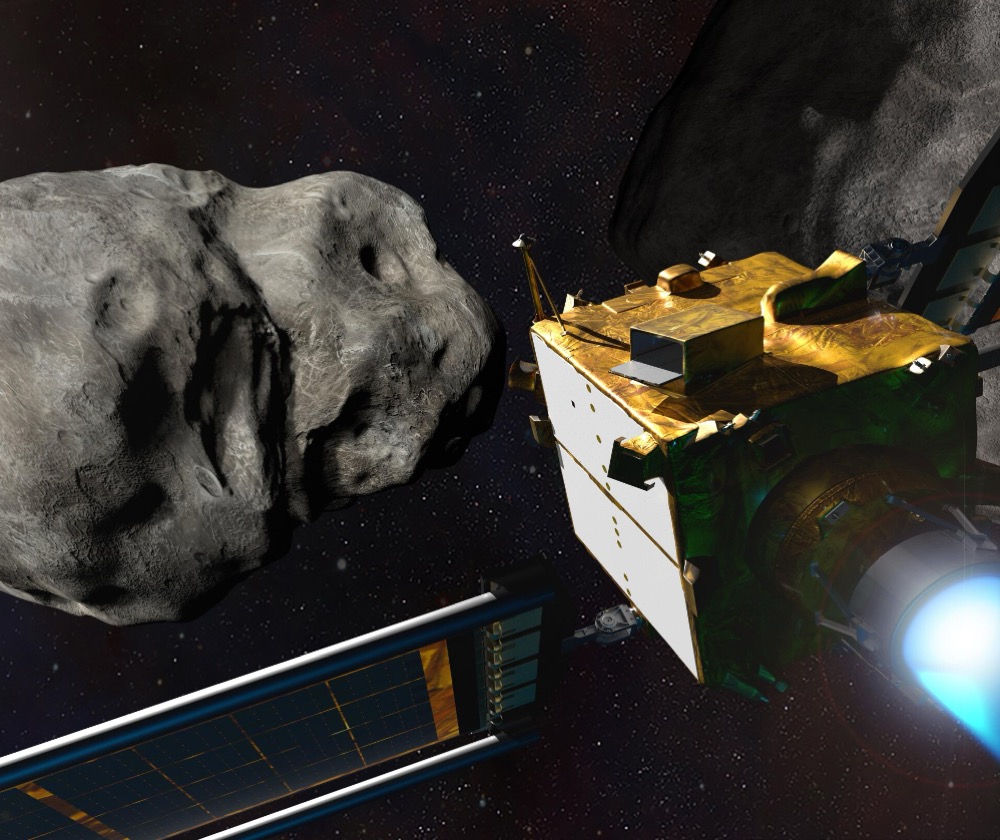
Major impacts from asteroids have happened throughout Earth’s history and will happen again in the future. Impacts big enough to affect large populations of humans are extremely rare, and currently there are no known objects threatening us for the next 1,000 years. But, considering the devastating consequences, we’re not taking any chances. NASA’s Planetary Defense is scanning the skies and creating a plan of action should anything dangerous be found. Blowing up an asteroid, like in movies, is not a good idea. It would likely take more energy than all weapons on Earth combined, and could send many smaller but still threatening pieces hurdling toward us. Instead, the plan is to find the threat early enough that a small nudge will throw it off course, missing Earth entirely. The DART mission was the first test of this method, and in 2022 it successfully crashed a spacecraft into an asteroid and measurably changed its motion.
Read More
Latest News About Asteroids and Comets
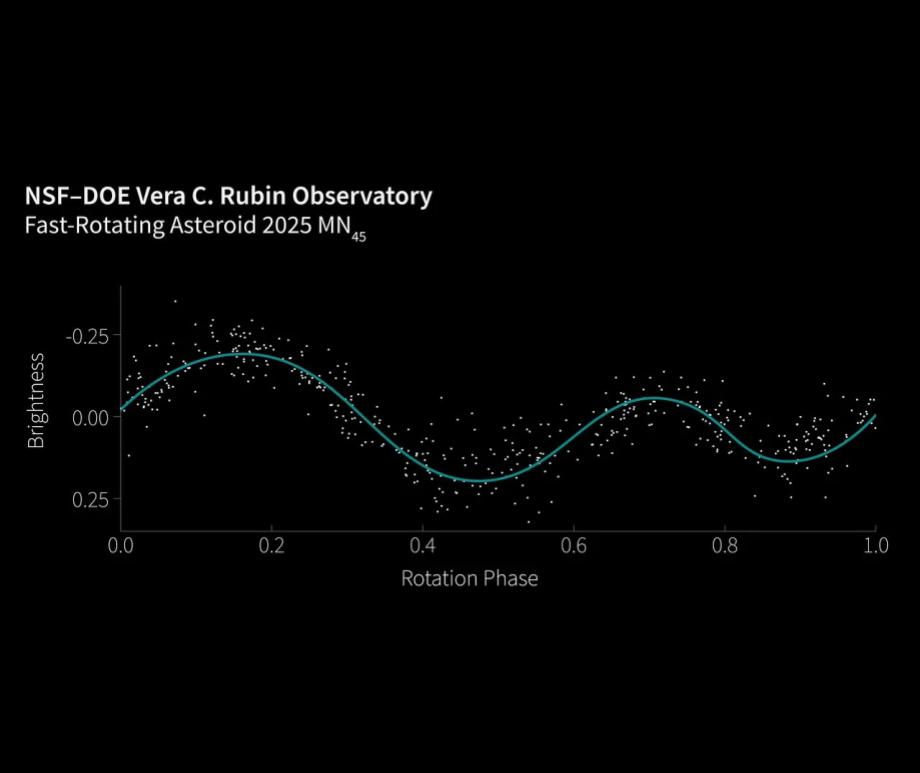
Record-breaking asteroid spotted in pre-survey observations
January 7, 2026
LSST Camera data has identified an asteroid, nearly the size of eight football fields, rotating every two minutes.
Read more
We've now found 40,000 asteroids that could pose a threat to Earth
December 16, 2025
Here's why it's the tip of the iceberg.
Read more
NASA's DART impact permanently changed the shape and orbit of asteroid moon
November 19, 2025
Dimorphos may start to "tumble" chaotically in its attempts to move back into gravitational equilibrium
Read more
The asteroid belt is slowly vanishing, shedding dust and rocks
October 6, 2025
reveal our solar system’s history.
Read more
The asteroid belt's slow disappearing act
September 29, 2025
Researchers have calculated precisely how fast this depletion of asteroid belt material is progressing
Read more
Did the dwarf planet Ceres once host life?
September 9, 2025
Astronomers suggest chemical energy could have fueled microbes long ago.
Read more
Interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS could be investigated as it races past the sun
September 2, 2025
'This could be literally a once-in-a-lifetime opportunity'
Read more
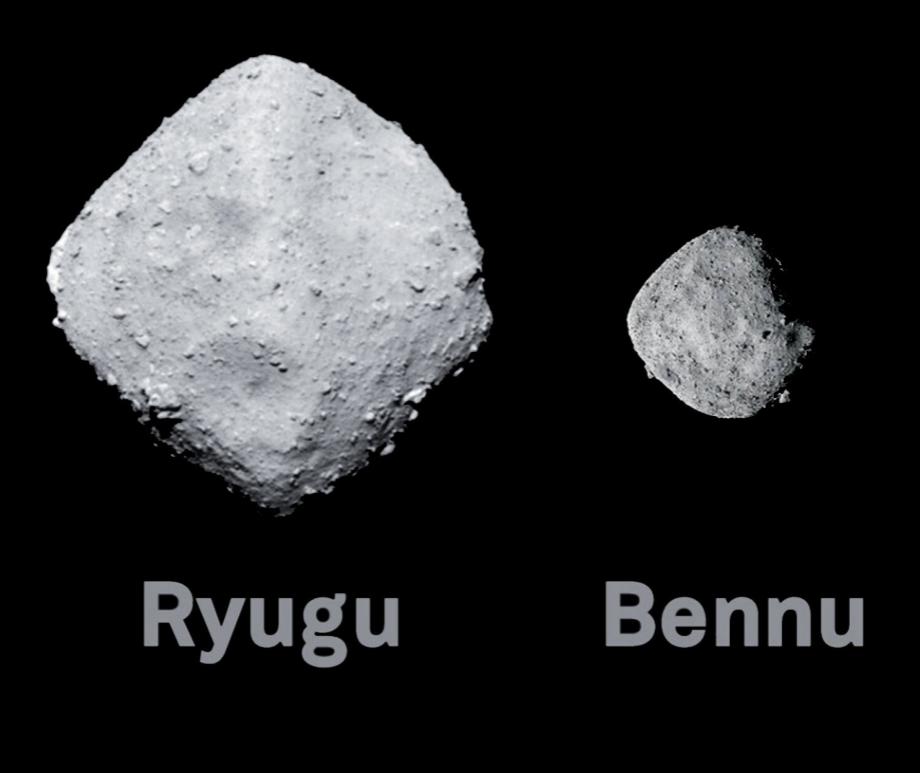
Spectral analysis suggests asteroids Bennu and Ryugu are part of Polana family
August 18, 2025
The asteroids were likely fragments from the Polana collision family
Read more
Tiny asteroids, big threats: how JWST is uncovering hidden worlds in our solar system
May 14, 2025
A study using JWST reveals a cluster of small, potentially dangerous asteroids
Read more
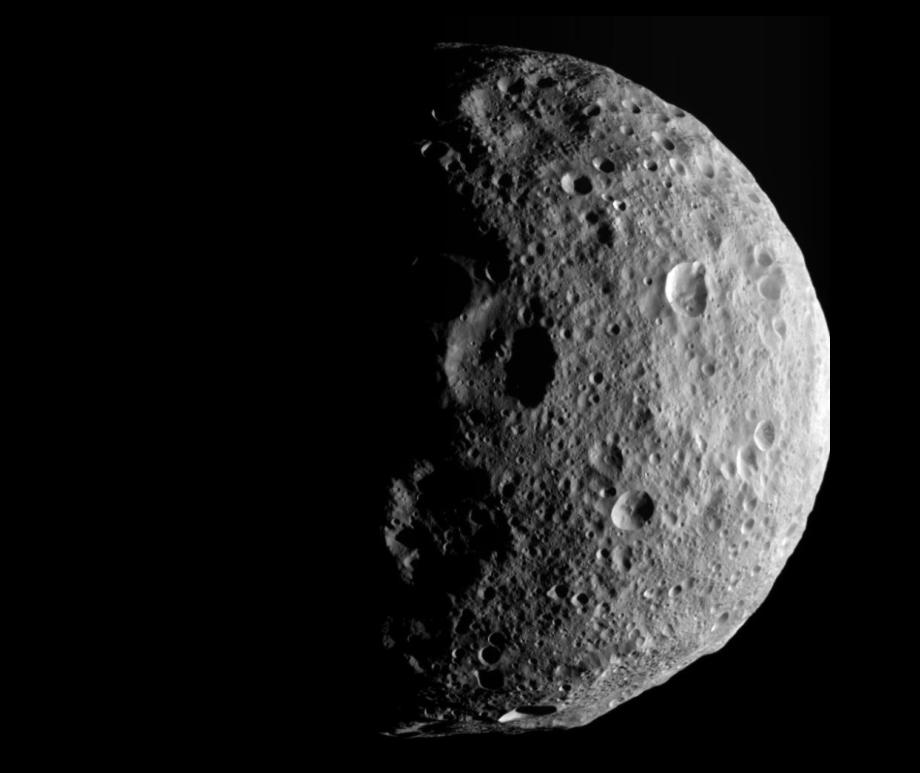
Vesta is simpler inside than previously thought
May 8, 2025
A recent study is forcing planetary scientists to reevaluate its internal structure.
Read more
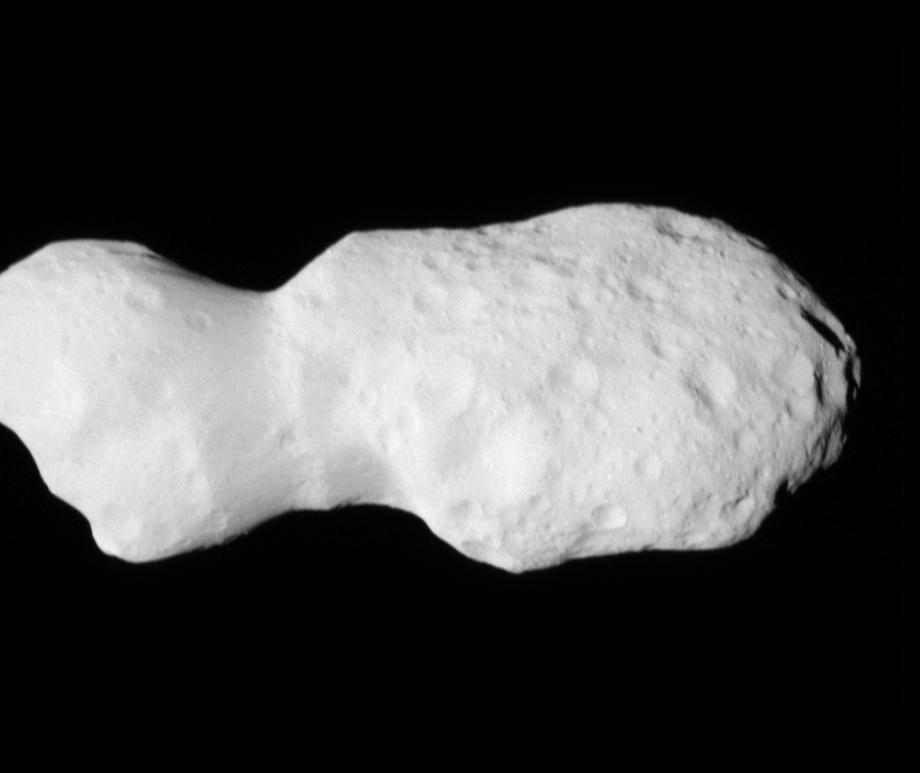
NASA’s Lucy Spacecraft Images Asteroid Donaldjohanson
April 21, 2025
The spacecraft’s closest approach distance was 600 miles (960 km), but the images were taken shortly beforehand
Read more
Near-Earth asteroid 2024 YR4 likely originated in Main Belt
April 14, 2025
Detailed analysis of the asteroid’s lightcurve points to origins from MAB
Read more
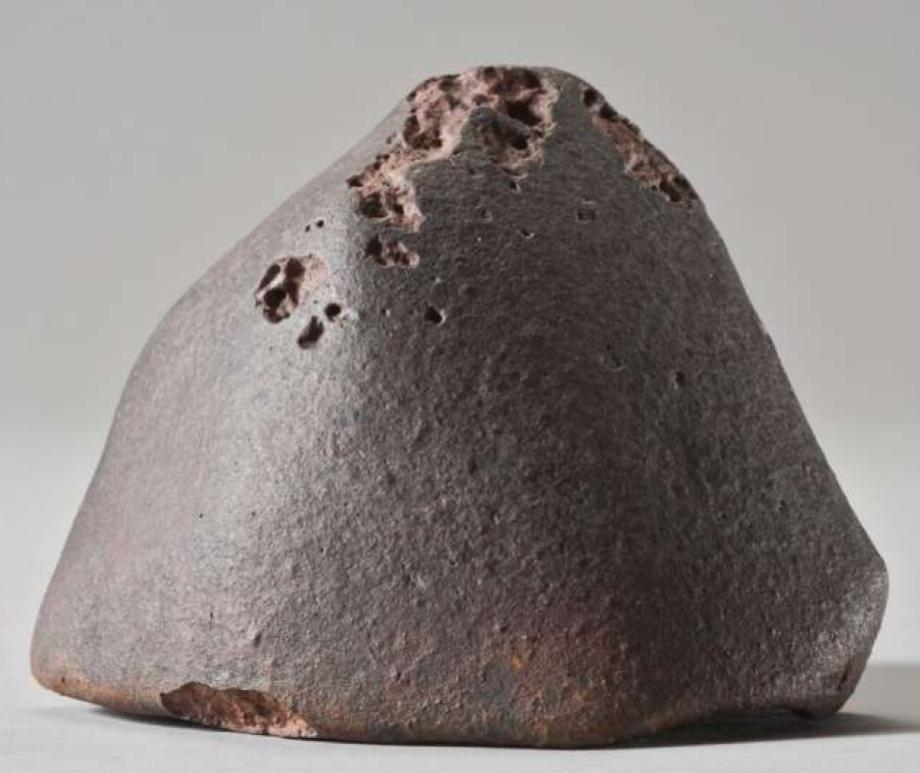
75 laboratory-classified meteorites traced to their parent asteroids
March 19, 2025
Astronomers from SETI Institute traced several previously unidentified source regions in MAB
Read more
Dramatically decreasing the time it takes to measure asteroid distances
February 14, 2025
It could contain insights into the origin of life on Earth
Read more
JWST finds the smallest asteroids ever seen in the Main Belt
February 11, 2025
Its unrivalled infrared prowess is helping it contribute to another important goal: defending Earth
Read more
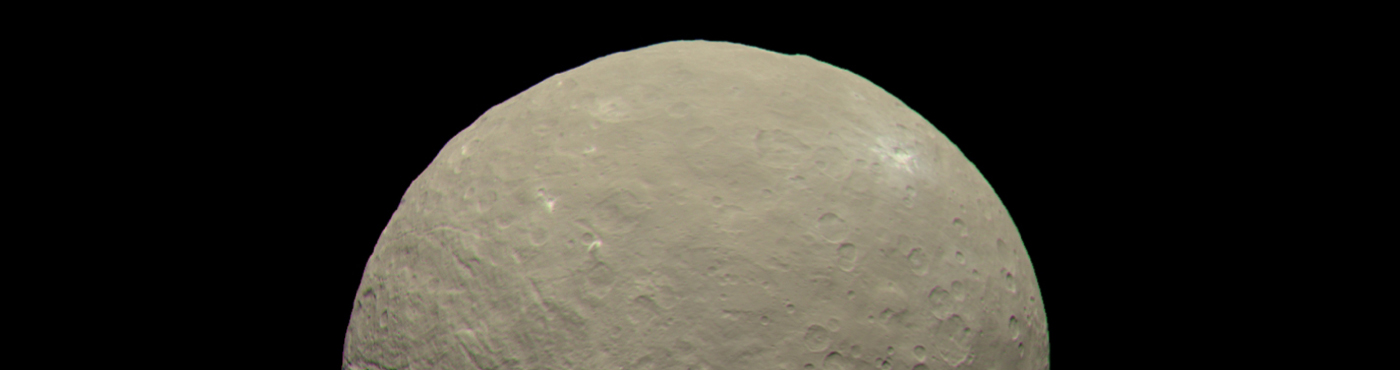
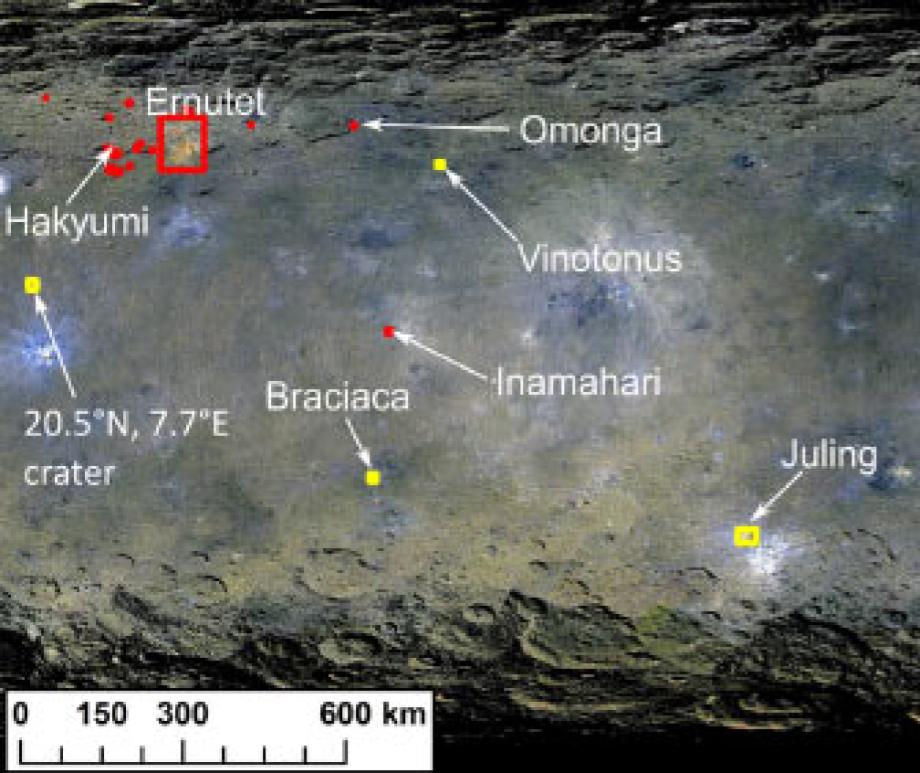
Ceres’ organic matter was originally delivered by impactors from Main Belt: study
January 28, 2025
Ceres is the largest object in the main asteroid belt, and the only potential ocean world in the inner Solar System
Read more
Astronomers discover 7 new 'dark comets,' but what exactly are they?
December 12, 2024
Dark comets look like asteroids but move like comets, without the trademark tail
Read more
MIT astronomers find the smallest asteroids ever detected in the main belt
December 9, 2024
The team’s detection method could aid in tracking potential asteroid impactors
Read more
New evidence of organic reservoirs found on Ceres
December 4, 2024
Ryugu's parent body appears to have had a fair amount of water present, too
Read more
Planetary scientists confirm new main-belt comet
December 3, 2024
A mysterious object discovered in the main asteroid belt in 2021 was determined to be a main-belt comet
Read more
Most of Earth's meteorites may have come from the same 3 spots
October 21, 2024
Until now, 6% of meteorites had been identified as coming from the moon, Mars or Vesta
Read more
Researchers trace 70% of meteorites to 3 asteroid families
October 16, 2024
These families were produced by three recent collisions, about 40 million years ago
Read more
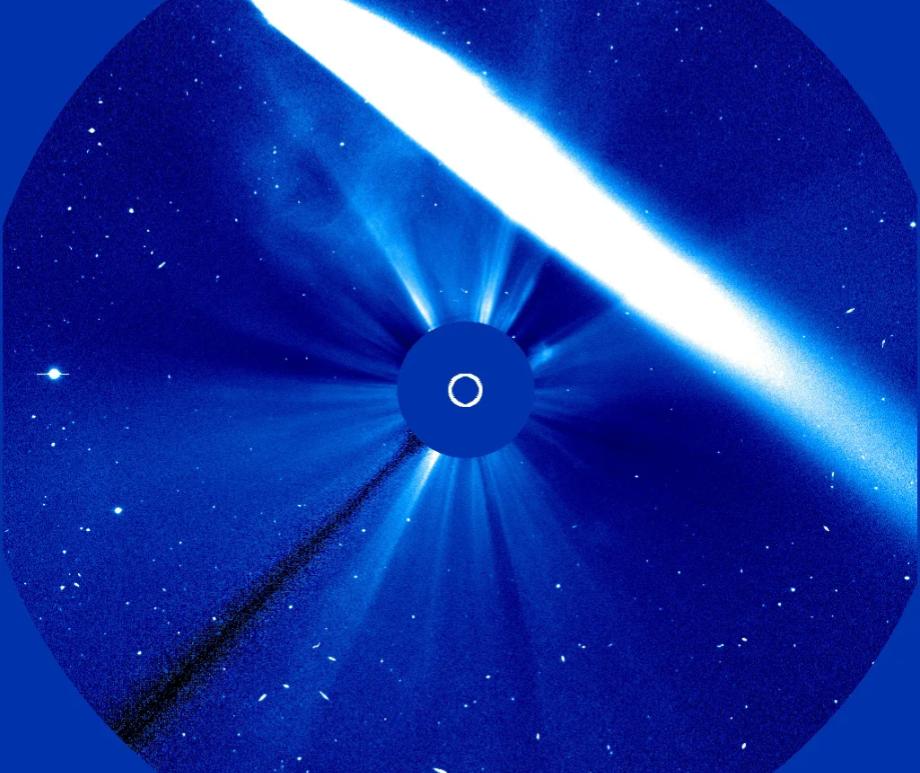
ESA/NASA's SOHO spies bright comet making debut in evening sky
October 11, 2024
The ESA and SOHO has captured images of the second-brightest comet to ever pass through its field of view.
Read more
Ryugu sample analyses show asteroids may have delivered compounds needed to start life on Earth
October 8, 2024
A team of researchers describes their study of a small sample of material collected from Ryugu.
Read more
Dwarf planet Ceres might have been a muddy ocean world
October 4, 2024
Ceres might have been an ‘ocean world’ but with a dirty, muddy ocean.
Read more
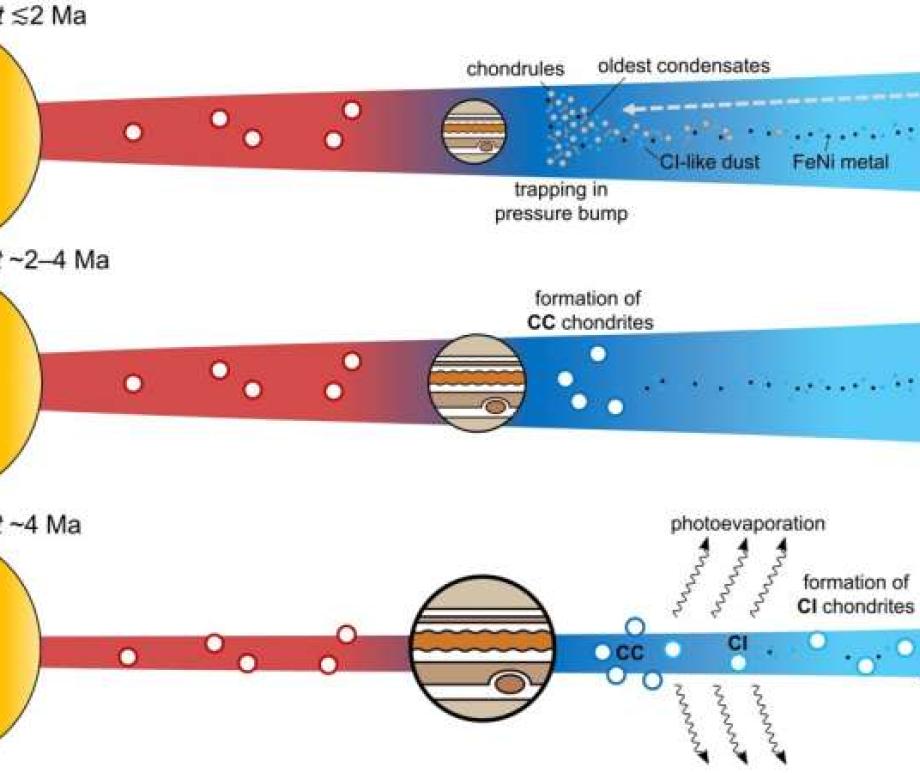
Ryugu samples call into question previous ideas about the formation of carbon-rich asteroids
September 27, 2024
New research suggests that Ryugu was formed near Jupiter.
Read more
2nd Kuiper Belt? Our solar system may be much larger than thought
September 18, 2024
Eleven objects found at the extremities of the solar system could mark the location of a 'Kuiper Belt 2.'
Read more
Actually, Ceres might have formed in the Asteroid Belt after all
September 18, 2024
Thanks to a deeper analysis of NASA's Dawn data, Consus Crater could point to Ceres’s origin in the Asteroid Belt
Read more
Jupiter’s moon slammed and tipped by giant asteroid?
September 5, 2024
4 billion years ago, a behemoth asteroid – perhaps 20 times larger than the dinosaur-killer – slammed into Ganymede
Read more
Fascinating Facts About The Main Asteroid Belt
- The asteroid belt is estimated to contain between 1.1 and 1.9 million asteroids larger than 1 kilometer in diameter and millions of smaller ones.
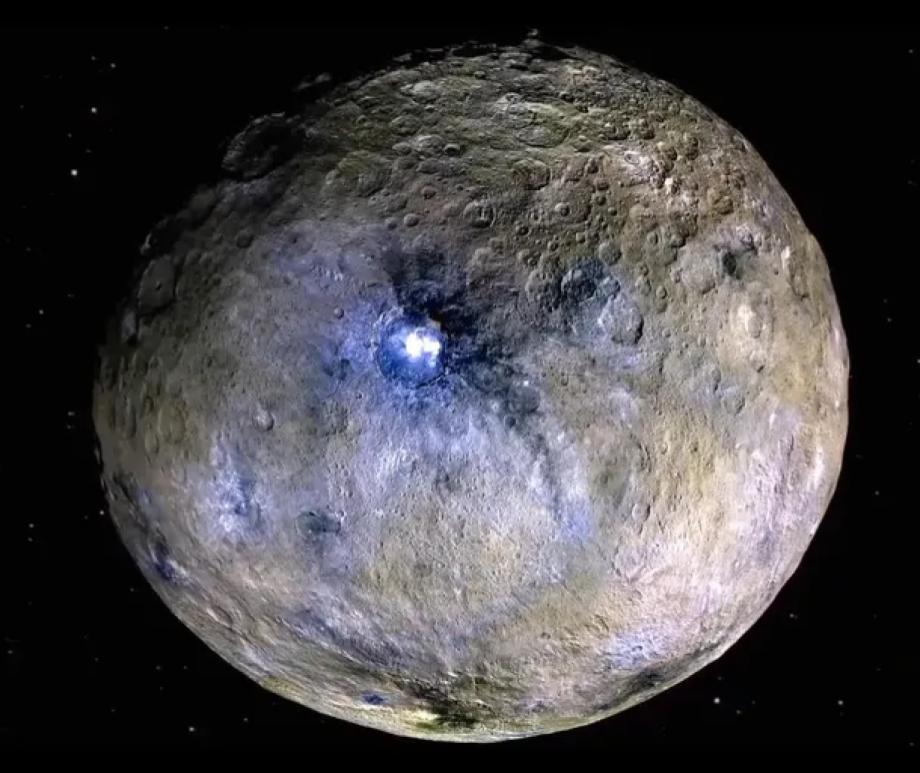
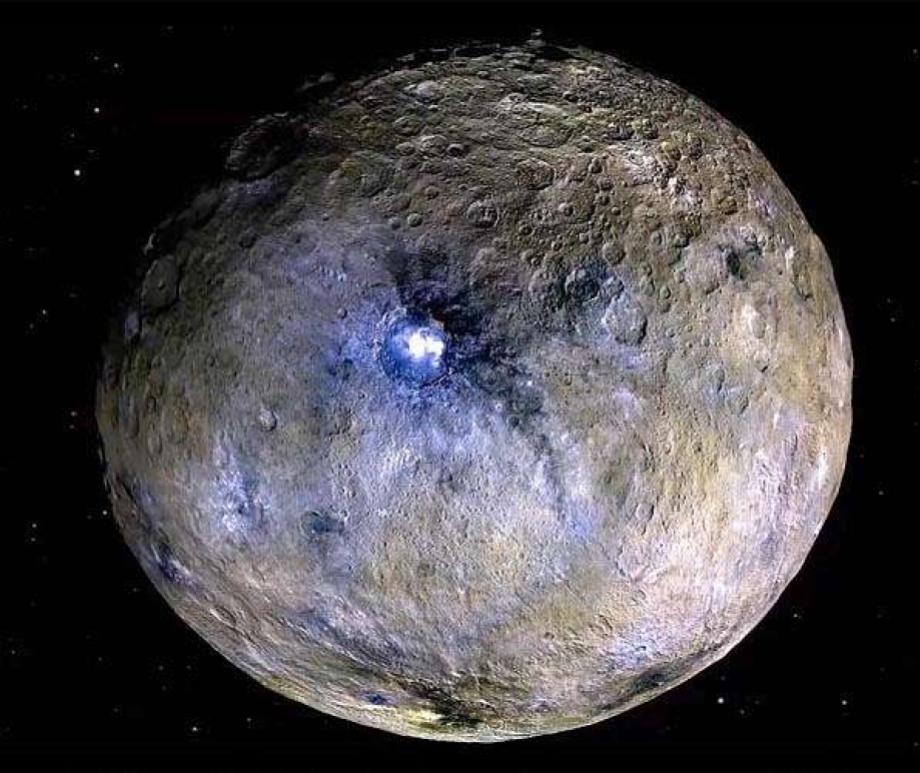
- Ceres is the largest asteroid in the inner Solar System and the only one classified as a dwarf planet.
- Ceres, Vesta, Pallas and Hygiea contain about half of the mass of the entire asteroid belt.
- The average distance between two asteroids in the belt is about 950,000 kilometers.
- Kirkwood gaps in the asteroid belt are relatively empty regions thought to be a result of Jupiter’s gravitational pull and correspond to the planet’s orbital resonances.
- Ceres is the only object in the asteroid belt known to be in hydrostatic equilibrium, meaning its own gravity causes it to be roughly spherical in shape.
- Ceres is the only object in the asteroid belt where water has been discovered; the water is seen as vapor rising from the surface, possibly from erupting icy volcanoes.
- Vesta is the brightest asteroid in the Solar System and the only object in the asteroid belt visible from Earth without a telescope.